Energy, Work and Power in physics.
Energy, Work and Power, some physical definitions
Energy, Work and Power are closely related physical quantities.
Energy
Energy is the capacity of a system to produce work. A system that has a certain energy will not do any work until that capacity is converted into motion. For example, an apple on a tree has a potential energy, but it does not do any work until it falls.
Its unit in the international system is the Joule (joule) which is the work done by a force of one newton whose point of application is displaced by one meter in the same direction.
Work
Work consists of a transfer of energy between systems. In the case of a force acting on a body, its work is equivalent to the energy required to move it. A force acting on a body is then said to do work when it causes a displacement of the body in the direction of the force. Therefore, in a mechanical system, if there is no displacement, the work is zero. This conclusion is not valid for thermodynamic systems, where heat transfers are considered as energy transfers.
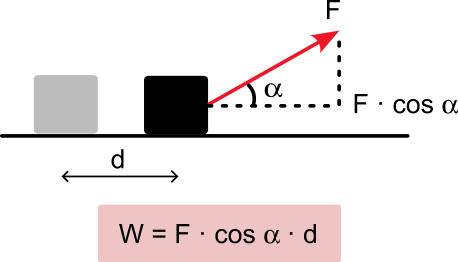
Work has the same units as energy.
Power
we can define power as the amount of work or energy use we perform in a given time. It is the speed at which we perform work or use energy.Units: watts.One watt of power is generated when work is done that consumes 1 Joule of energy during 1 second of time.. 1 w = 1 joule/ 1 segundo
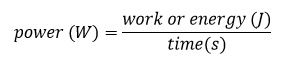
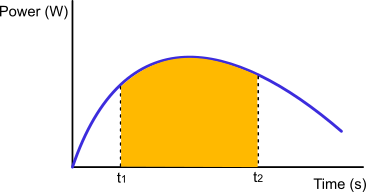
Graphical interpretation of energy in the power chart
Graphically, energy is the area under the graph of power as a function of time:
Sicami Tracks - Start